How Important Are Ants In Ecosystems?
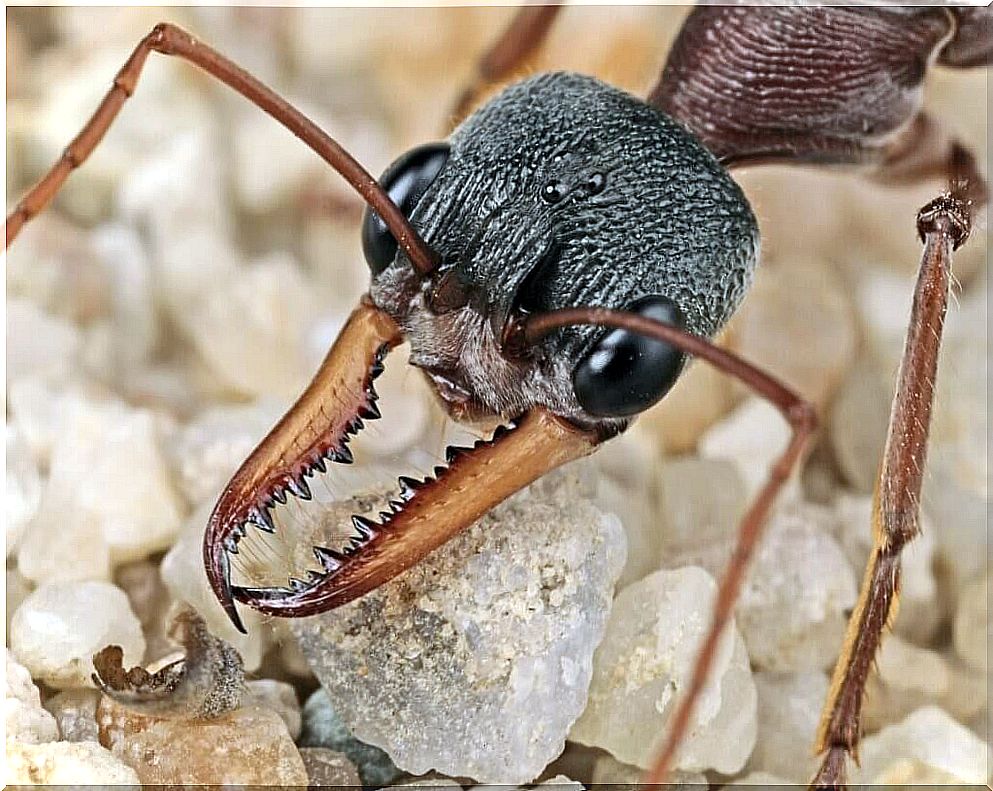

Ants, like all animals on planet Earth, are of constant importance: they are not here simply because they are, they are an active part of an ecosystem that feeds on every living thing that is part of it. Its specific origin is a mystery, as is the origin of humanity itself, but phylogenetic studies are increasingly bringing us closer to definitive answers.
What is known is that these insects date from about 90 million years ago and belong to the ant family, whose bodies have antennae and are divided into 3 sections, characterized by having a small waist. They are relatives of bees and termites, and it is estimated that there are about 13 000 species distributed almost all over the planet.
Another of its specific characteristics is its behavior: ants usually have only one queen, with a system of workers that maintain the community. They usually appear in large groups and for many are a type of pest, but this is because their importance in the ecosystem is disregarded. As we will see in the following lines, the work of these invertebrates is priceless.
The importance of ants in ecosystems
Ants are of great importance in ecosystems, as they play an essential role in their regeneration. Their pivotal role is unnoticeable to human eyes, but that doesn’t mean they aren’t doing their part day and night. Ants have a hierarchical organization in which, as experts explain , each ant adopts a biological role.
The workers are those who go out to work in order to maintain the well-being of their community. In the task of going out in search of food, they disperse seeds, prey on arthropods and disperse insects in the roots. Access to the resources that ants provide to plants depends on this organization.
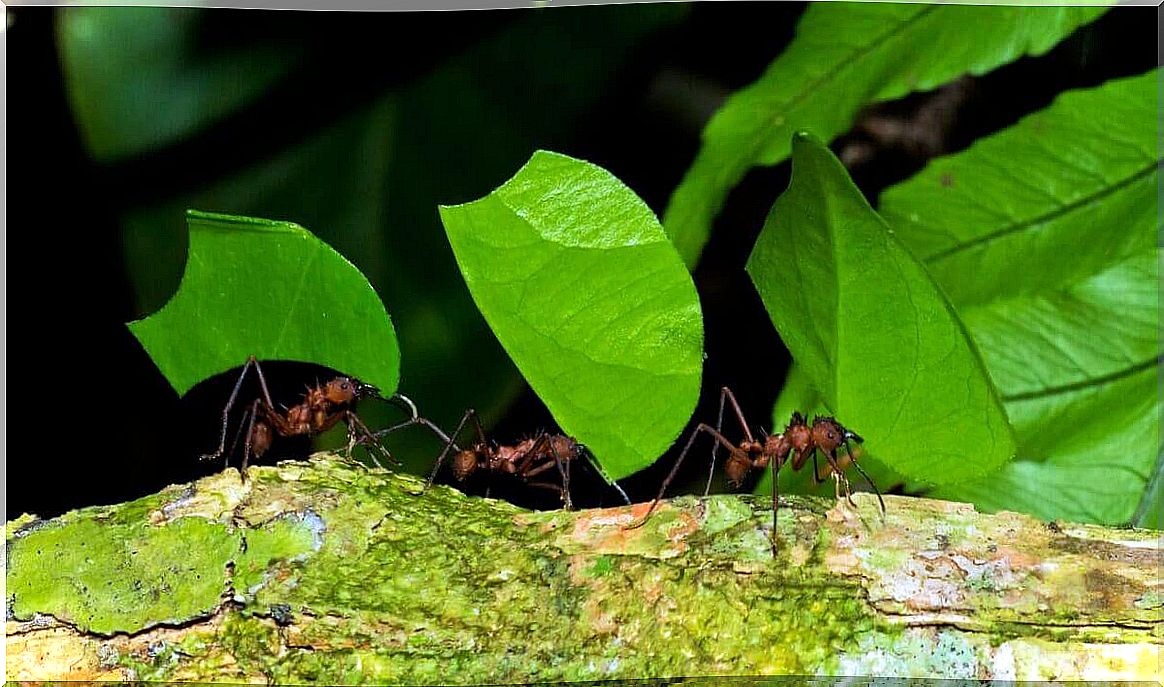

What are the types of interactions between ants and plants?
The relationship between ants and plants is very close, as they depend on them to survive. In fact, some plants have developed ways to attract ants through the nectar from their flowers, stems and thorns. Experts argued that plants use ants to propagate their seeds and defend them from predators.
Next, we will describe in a little more detail the different types of interactions between plants and ants, which in turn contribute to the preservation of ecosystems. Check out!
Neutralism
This type of relationship does not benefit or harm plants or ants. In other words, it is a neutral mode of interaction in which there are no repercussions of any kind. It may be that a neutral interaction is really neutral, or that scientists may not have discovered an underlying mutualism.
antagonistic
Studies have identified the antagonistic relationship as one in which there is predation on seeds by ants, which cut the leaves and remove the nectar or pollen from the plants. Specifically, this type of interaction refers to a negative or harmful relationship between ants and plants.
Mutualists
Research asserts that the mutualistic relationship between ants and plants is one of the most fascinating fields of study for naturalists and ecologists around the world. This interaction is based on the defense that ants provide to plants, as they are ‘anti-herbivores’.
The ants’ gain or reward is nutrition, since the plants are the mainstay of their diet, feeding on their nectar and waste. Furthermore, they serve as a shelter. On the other hand, plants gain protection and growth, as parasites on their surface can be preyed upon by workers.
The importance of ants: other functions in ecosystems
As you can see, ants have different roles within ecosystems. In addition to their relationships with plants, let’s talk about some of their other important functions.
soil modification
Soil aeration is one of the transformations made possible by ants, demonstrating once again their importance in ecosystems. By creating underground colonies filled with galleries, tunnels and chambers, they aerate the substrate and enrich it with the nutrients they carry from the plants and the food they obtain.
According to some research, Darwin was the first to talk about this genesis and modification of the soil of which ants are a part. Without them, the biogeochemical cycles of environments could not be carried out properly.
Degradation of organic matter
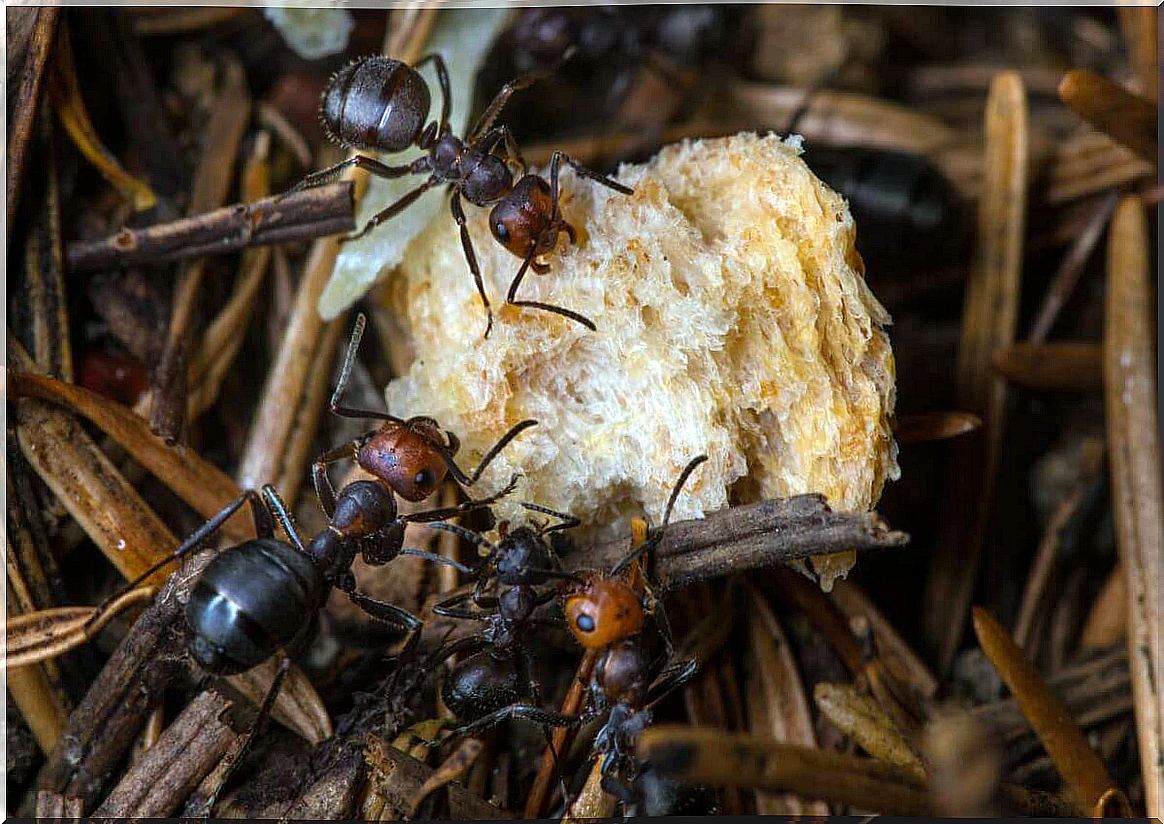
Soil organic matter includes common organic components, dead roots, plant and animal waste and decomposition products. By feeding on many of these organic components, ants contribute to their degradation.
Nutrient transport
As we have already mentioned, ants build their colonies underground from chambers and tunnels, through which they transport plant nutrients and other food sources. Although some build their nests in trees or branches, these ‘buried cities’ are the strategy followed by most species.
In this way, there is a benefit for the ants, who obtain good food, and another for the plants, as they extract their nutrients from the same soil in which the colonies live. It is practically a cycle in which the benefits are multiple. This is one of the examples of the mutualistic relationship that exists between the two groups of living beings.

Food for other species
As studies published in Springer Link indicate , the death rate of queens before founding a colony is very high. During the nuptial flights, thousands of winged ants take flight and participate in mass fertilization events.
This is an excellent source of protein for many birds, reptiles, amphibians and other invertebrates, who eagerly await the first spring rains and the ants’ subsequent nuptial flights. The small percentage of queens that survive this stage will found a new colony and the cycle will be restarted.
The importance of ants: what happens if they disappear?
The importance of ants is such that if they disappeared tomorrow, global chaos would begin to form. Ecosystems would be the main victims of deterioration. Many plant species would go extinct, while the soils would begin to fill with insect corpses, contributing to the harmful accumulation of organic matter in the soils.
Importance of predatory ants
Solenopsis cf. picea is the name of one of the predatory ants. According to articles, this species is widely distributed in the Risaralda coffee zone, in Colombia. Even as a predator, this ant is extremely important, as it performs essential biological control.
Although it is a generalist and predator of several species of insect pests, it plays an important role in the corn and pumpkin agroecosystems in southern Mexico. One more reason why they cannot disappear, neither this species nor any other.
There are also other ants that feed exclusively, or almost exclusively, on insects, such as those belonging to the genera Harpegnathos, Odontomachus and Myrmecia , among others. These small hunters are essential to regulate the presence of other invertebrate species in small-scale ecosystems.
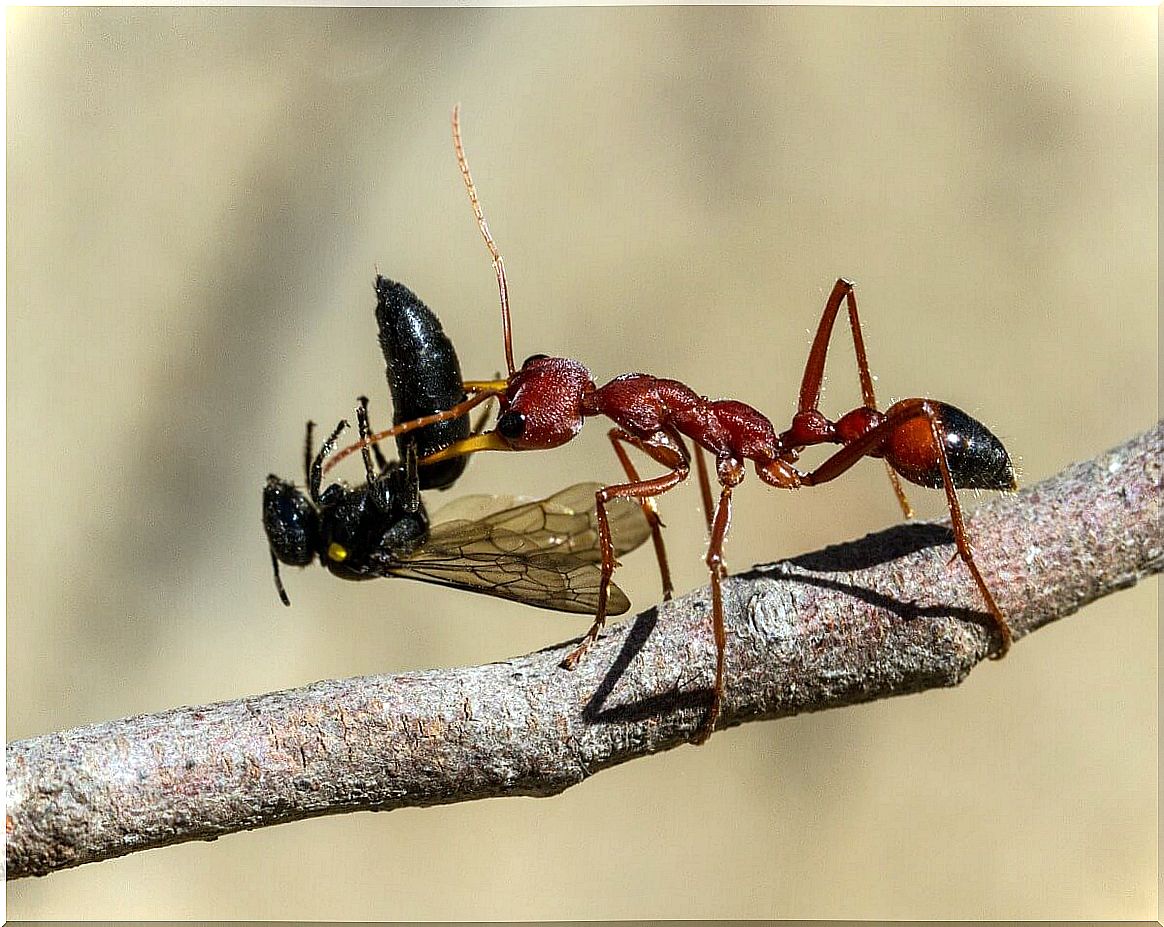

As you can see, the overall picture you get of ants is sometimes a little skewed. Some cut leaves and devastate entire crops, others wipe out pests using their lethal jaws and stingers, and still others maintain functioning biogeochemical cycles by returning many nutrients to the soil that would otherwise be lost.
If something became clear to us after reading this, it is that any species endemic to an environment is essential for the maintenance of its ecosystem. Although we don’t know all about how ants work, nature is wise and has provided their permanence over the centuries for good reason.